See Solution
Wastewater Monitoring System
Smart water systems are based on the combination of Internet of Things (IoT), big data and AI technologies can help monitor processes and quality, and hence provide end users with the capacity to make informed decisions based on real-time data.
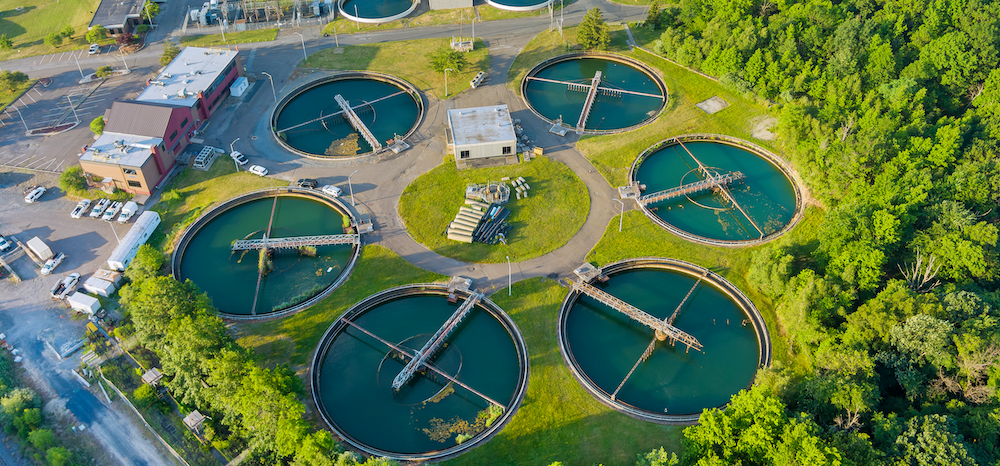

The Solution
Sensor IT designed a Wastewater Monitoring System based on IoT components to monitor the Mombasa sewer system. The Mombasa sewer system was faced with numerous challenges arising from prolonged use and overload. Our solution aimed to improve the system’s overall efficiency by preventing overspills of water and sewer blockages., and this was envisioned by implementing a state of the art, IoT solution, entirely designed and manufactured in the UK by Sensor IT.
The Wastewater Monitoring System was sponsored by Innovate UK (news post) was named Maji Taka Tech. WASREB (Water Services Regulatory Board) indicated in their 2020 Impact Report that “Utility efficiency is key to attaining targets”, these targets being Sustainable Development Goal 6 and the National Vision of Kenya committing to the universal access of water and sanitation by 2030. As of 2019, Mombasa is ranked last out of the 12 ‘very large WSP utilities’. Chances of sufficient investment in the sewer system remain unlikely therefore it is crucial to improve pre-existing infrastructure to increase its efficiency.
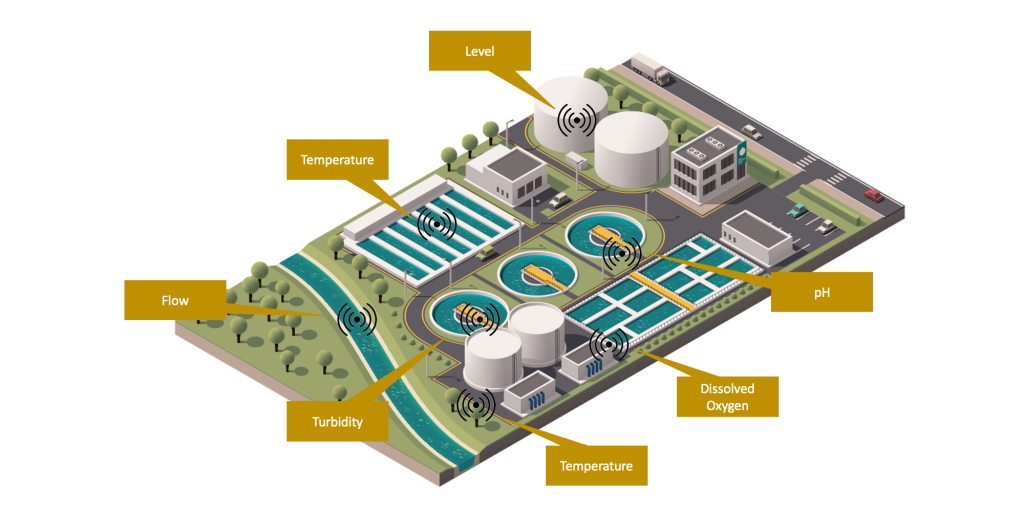
Wastewater Monitoring System Technical Details
The Wastewater Monitoring system included multiple endpoints to measure the wastewater flow in several locations and the development of a real-time dashboard to monitor this flow. The system’s deployment set a precedent for future enhancements and streamlining of wastewater treatment operations. It’s important to note that the technologies developed in this system are not only applicable to waste management but also useful for broader water utility applications where data is transmitted from the endpoint to the dashboard to better manage the overall apparatus.
For this solution, Sensor IT selected LoRaWAN® as the data communication protocol between the sensor endpoints and the central monitoring dashboard. This choice was driven by the limited availability of traditional communication infrastructure in the deployment areas, particularly in peri-urban and informal settlements where reliable cellular or wired connectivity is often lacking. LoRaWAN® offered a robust alternative by enabling long-range, low-power communication that does not rely on existing networks. This approach significantly reduced deployment costs, minimized energy consumption, and allowed for greater flexibility in placing sensors across geographically dispersed or infrastructure-poor locations. Furthermore, the protocol’s scalability and ability to support thousands of low-data-rate devices made it an ideal fit for real-time environmental monitoring applications in both urban and rural contexts.
Target Audience
This Wastewater Monitoring System was initially conceived to address water quality and availability challenges faced by local communities in Mombasa, Kenya. The solution focuses on real-time monitoring of key water parameters to support cleaner, safer, and more efficient water resource management. However, recognising that water is a globally shared resource—and that the pressures on water systems extend far beyond wastewater—we have expanded the system’s scope. It now supports a range of water-related operations including freshwater supply, environmental monitoring, and industrial process oversight.
This project has been supported through a grant awarded by Innovate UK, delivered in partnership with Connected Places Catapult as part of the Urban Links Africa programme (https://cp.catapult.org.uk/news/urban-links-africa-open-call). Urban Links Africa fosters collaboration between UK innovators and African cities to co-develop smart city solutions that address urban challenges in energy, mobility, waste, and water. By participating in this programme, Sensor IT has been able to pilot and scale this water monitoring innovation in a real-world urban context, with potential for both local impact and global application.